Businesses cannot afford to make decisions based on gut instincts or assumptions and data-driven strategies rooted in specific customer data is a key in winning the competition and being successful in marketing. Comprehensive customer analytics holds the key to deeply understanding your audiences, crafting tailored customer experiences, and serving customers in a highly personalized manner.
However, collecting customer data involves privacy, security, and transparency responsibilities. Businesses need to be careful in what data they collect, how they collect them, and how they handle customer data management. When harnessed correctly, insights from customer interactions become an invaluable asset driving improved marketing ROI, increased conversions, lower churn, better product-market fit, and revenue growth.
It’s important to fully understand the importance of customer data, how to collect it, types of customer data management systems, how to analyze and extract insights from data sets, top practices for managing and protecting customer data, and finally the benefits of data collection for consumers.
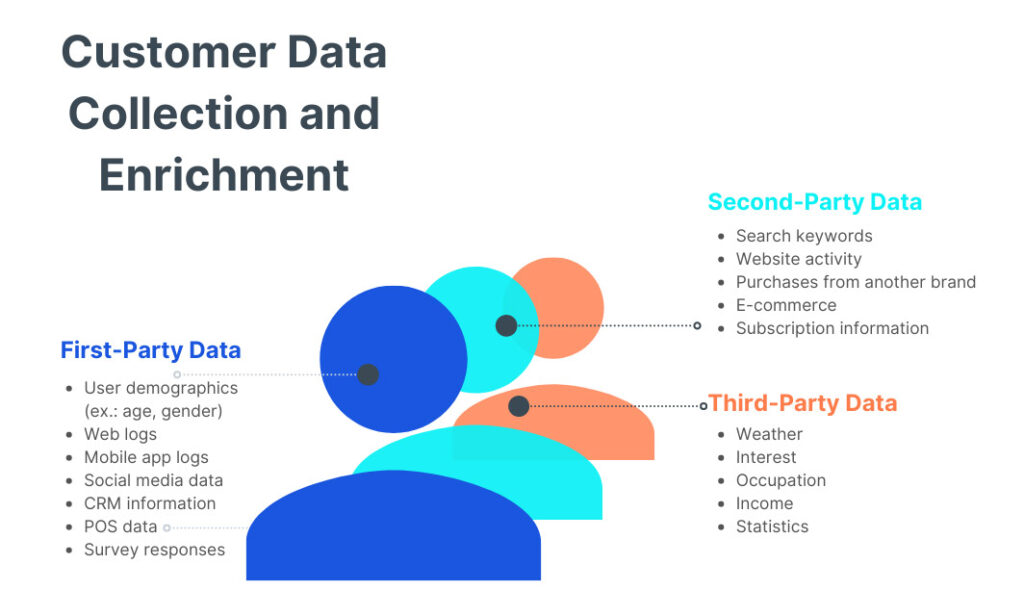
Image Source: treasuredata.com
Customer data refers to any information related to customers and their interactions with a business across touchpoints, including sales and marketing data. More specifically, customer data can be divided into three main categories:
This data you can collect by conducting customer analytics on various sources like websites, mobile apps, offline purchases, customer service channels, and more. You can collect customer data both quantitatively and qualitatively.
The goal is to compile a 360-degree customer profile with data from all sources that covers demographics, behaviors, and attitudes. This complete view allows businesses to hyper-personalize experiences and marketing throughout the customer lifecycle.
There are several compelling reasons for businesses to collect customer data actively:
Ultimately, leveraging insights from customer data leads to better experiences, retention, and cash flow. Comprehensive, unified data informs business decisions across all customer-facing teams.
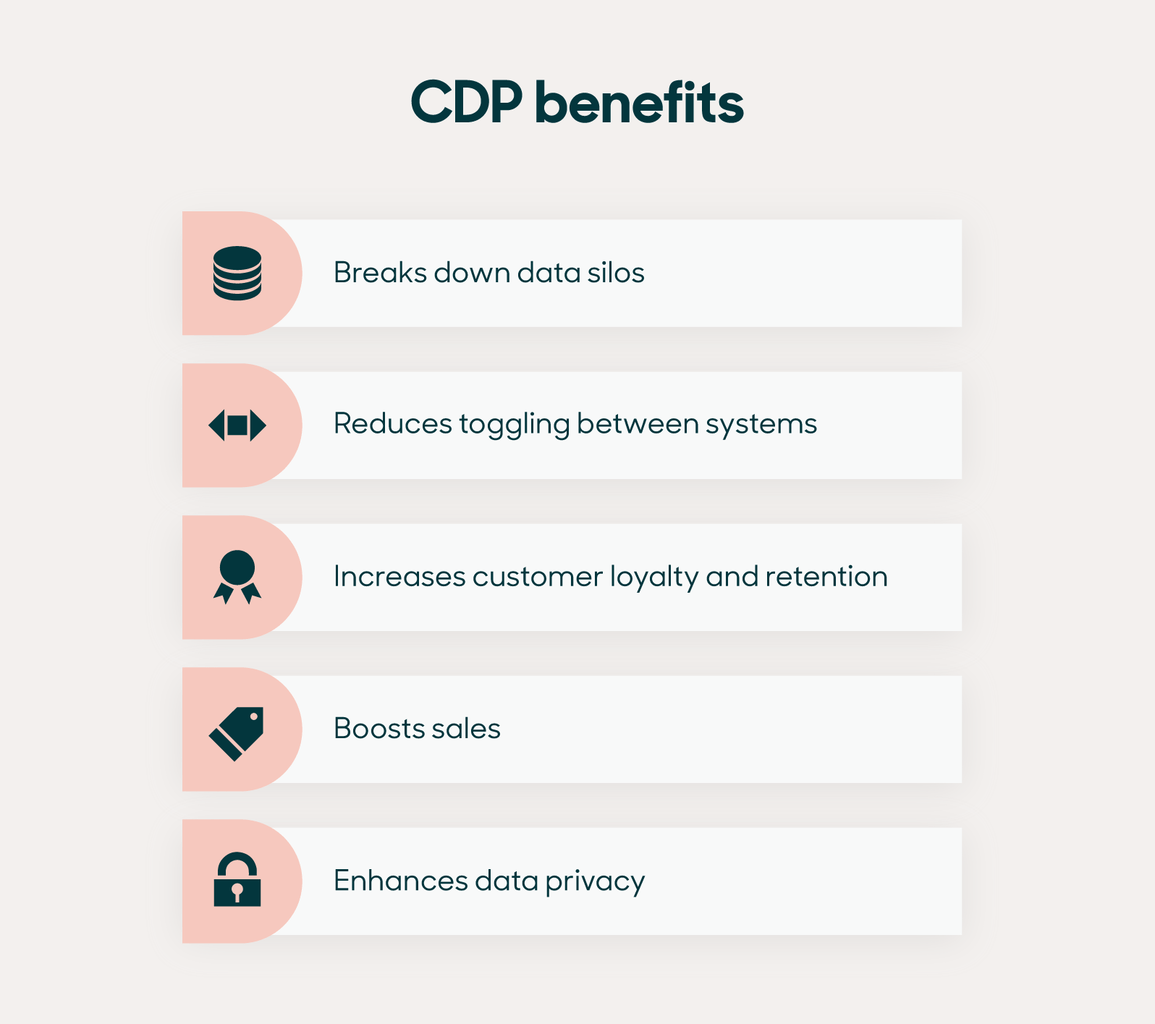
Image Source: zendesk.com
While customer data delivers tremendous business value, there are a few key considerations before jumping into the details of how to collect customer data.
Therefore, approach customer data collection ethically with water-tight governance processes around consent, privacy, security, and transparency. Customer data can become one of the most valuable business assets with proper care.
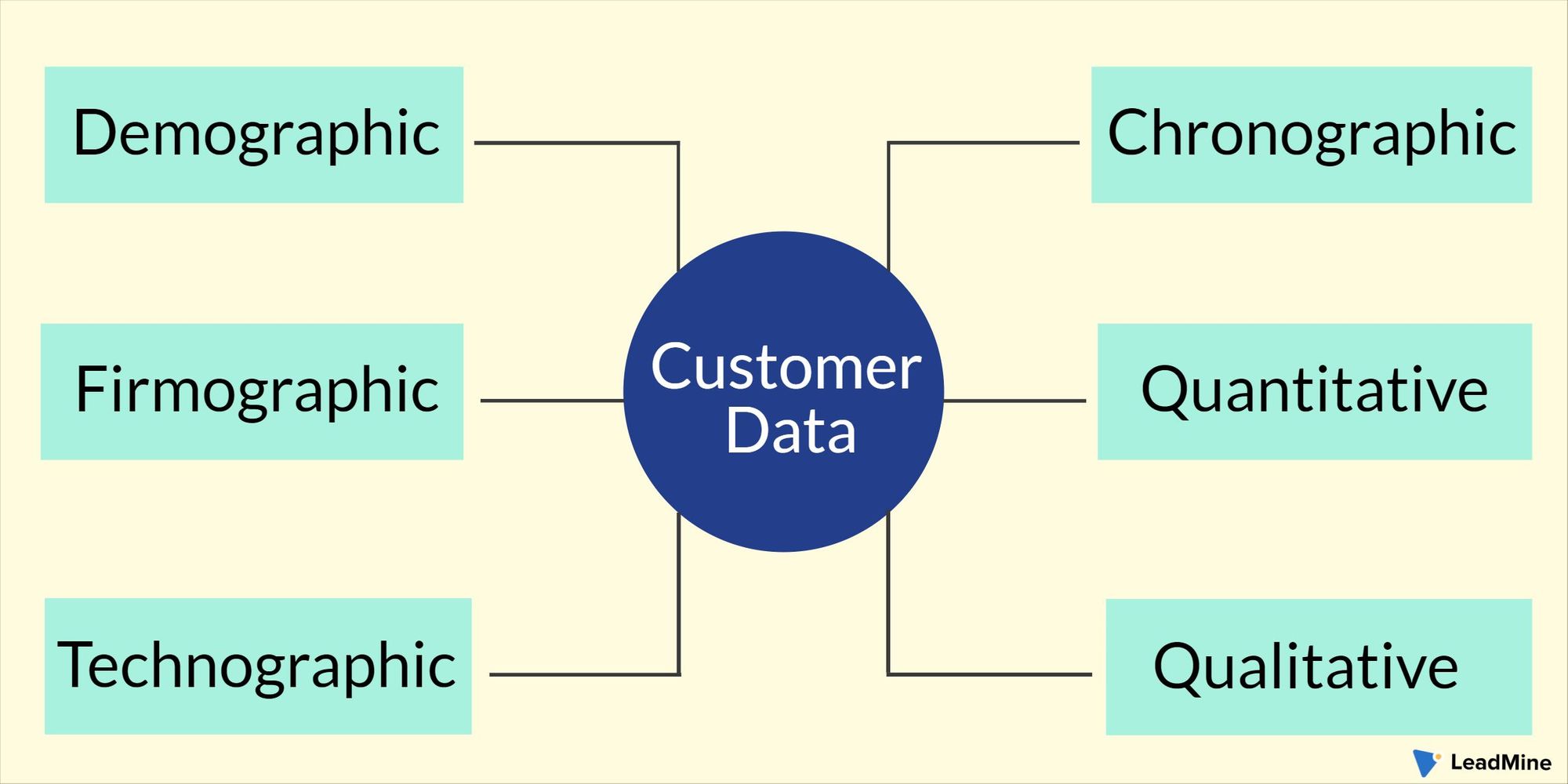
Image Source: leadmine.net
There are four high-level categories of customer data that modern businesses should aim to collect and connect:
This includes personal details like name, contact information, demographics, etc. There are two sub-types:
Within Non-PII, further subcategories emerge:
Customer data about user behavior shows how customers interact with a company’s products, services, and channels, including:
Direct customer opinions, perceptions, and preferences gathered via:
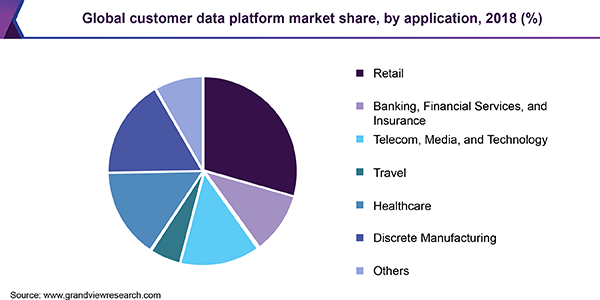
Image Source: grandviewresearch.com
There are various methods and data sources for collecting customer data, typically grouped into:
For top of sales funnel visitors just entering the site or ecosystem, the emphasis should be on frictionless interactions to gradually collect customer data over time. Online Forms are one of the most effective channels for converting unknown website visitors into known contacts by capturing leads. Useful top-of-funnel form tactics include:
For leads who have engaged but not yet converted, go more in-depth by:
For existing customers and repeat purchasers, actively collect data through:
The methods and sources used should map to the data type needed at each customer lifecycle stage. Ensure that data collection is tailored to avoid overwhelming customers.
As for existing customers, actively collect data through:
Additionally, it’s helpful to use periodic outreach for more qualitative insights:

Image Source: lexer.io
Now, let’s explore some of the top sources and techniques on how to do proper customer analytics and how to collect different types of customer data.
Install robust customer analytics platforms like Google Analytics on all websites and mobile apps. The tracking code passively collects incredibly detailed behavioral data on all user activity, down to individual clicks, taps, page views, button clicks, site searches, and more.
Website analytics provide a goldmine of insights around content engagement, site navigation patterns, conversion funnels, usage by device types, visitor demographics, and much more; trend analysis over time is pivotal.
Online forms are highly effective for converting website visitors into known contacts by capturing lead data. Form analytics data should be added to all web forms to:
Afterward, integrate form data into the central CRM system for a unified customer record. For example, an insurance company can add a web form offering a policy quote in exchange for name, email, and details.
Some key form data points to analyze include submission volumes, conversion rates, abandonment points, completion rates, field inputs, response times, and campaign integration. The goal is to gain insights into visitor behavior and the quality of the generated leads. Ensure that forms are optimized continuously based on the data.
Actively ask for structured customer feedback through online surveys, review forms, questionnaires, and interactive quizzes. Embed survey distribution on-site or sent via email campaigns. For example, a restaurant review site can email diners a 1-5 star rating survey one week after their visit. Always ensure to segment response data by attributes for deeper customer insights.
Live chat provides an engaging way to gather customer data through conversational interactions. For instance, chatbot questionnaires can qualify leads, while live chat agents handle complex issues. For example, a university chatbot could engage prospective students and capture customer data on their interests and goals. It is important to analyze chat transcripts to identify trends and gaps.
Social media offers a wealth of unstructured customer data. Brands could use social listening tools to monitor customer conversations, interests, and engagement patterns across platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, YouTube, forums, review sites, etc.
Key customer data to gather includes brand mentions, hashtags, shares, likes, comments, followers, influencer interactions, and customer feedback. Social listening reveals awareness, perceptions, product sentiment, emerging trends, competitive intel, and demographic insights from customers.
Social media monitoring tools like Hootsuite and Keyhole empower you to gather data across social platforms where customers interact. Track brand mentions, engagement metrics, followers, social conversations, and reviews. For example, a fashion retailer can track user-generated content about new product lines on Instagram to gauge appeal.
DYK, apparel #retailers including #Nike and #NorthFace share personal #CustomerData such as images & sexual orientation with third parties? 🛒
According to a study by @incogni_com. In total, 45 of 180 apps collect photos and nine collect search history. https://t.co/V8UXPbeyrq
— TechInformed (@TechInformed) January 24, 2024
Robust marketing analytics help connect campaign interactions to downstream conversions across channels. This requires tracking UTM campaign tags, landing page form data, and CRM integration.
Key data points to examine customer analytics include website traffic, form submissions, email open/click rates, content downloads, advertising reach/clicks, and ultimately sales influenced by each initiative.
Marketing automation platforms, such as HubSpot, connect campaign data across channels like email, paid search, display ads, social promotions, referrals, etc. For example, an automotive company can track web traffic, test drive requests, and purchases driven by email and paid search.
Collect key behavioral data with each transaction, subscription, and account registration, including purchase details, services used, churn risk metrics, product usage metrics, and profile information like demographics and preferences. For example, a SaaS company can link plan details and feature usage to customer profiles over time.
Carefully choose tools to gather, connect, and activate customer data management strategies from each source into a unified profile.
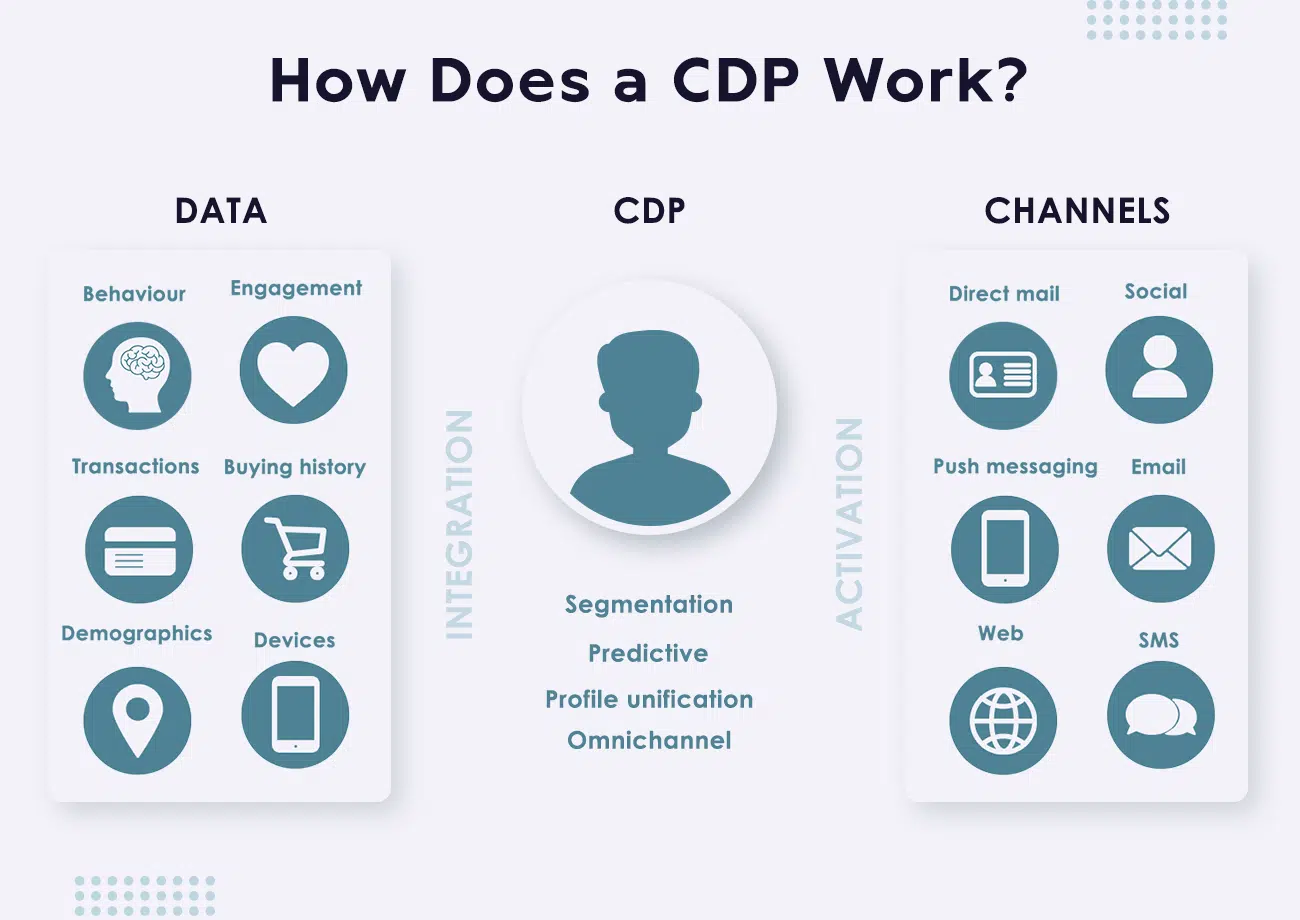
Image Source: thingsolver.com
While collecting customer data is crucial, the real value lies in deriving insights from customer data analytics and managing that data effectively. Follow these key steps to optimize customer data analytics:
Before starting the analysis, clearly define the business objectives, opportunities, or issues you want the data to address. This focuses the analysis on actionable insights tied to tangible goals versus just exploratory observations. For example, questions could include: Which customer segments have the highest churn risk? Which sales channels have the best conversion rates? Which products have the highest returns?
With goals defined, connect and prepare relevant data from sources that can credibly inform the business questions. For instance, analyze behavioral data from the website, mobile apps, transactions, chat logs, and surveys. Avoid blind spots by blending data sources.
Before concluding, thoroughly profile the compiled data for completeness, accuracy, and consistency. Identify and resolve errors, duplication issues, inconsistencies, or missing values through ETL (extract, transform, load) processes and quality checks; high data integrity is mandatory.
Leverage machine learning algorithms, predictive customer analytics, data mining techniques, and visualizations to analyze prepared data, identify meaningful patterns and trends, and quantify correlations related to business goals. For example, use customer retention models to determine churn drivers.
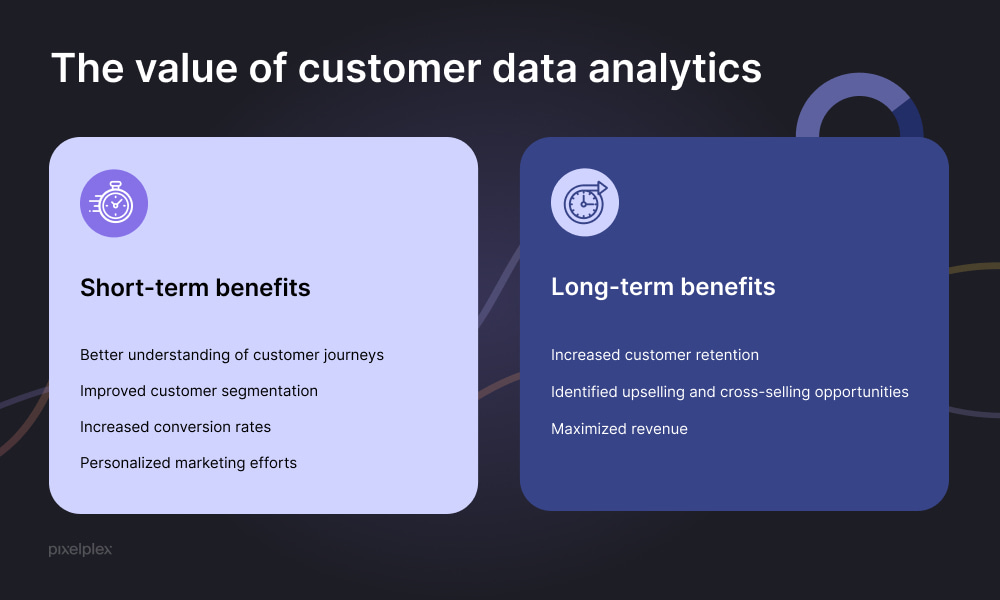
Image Source: pixelplex.io
Analysis is an ongoing process, not a one-off project. Continually monitor key metric trends to track performance. Refine analysis parameters, techniques, and data collection practices based on new requirements and set data analysis KPIs.
Customer analytics output should fuel tangible actions across marketing, product, operations, and other groups to drive growth. Communicate these findings through reports and presentations and build a data-driven culture that maximizes value from customer data; the ultimate goal is to turn analysis into action.
When harnessed correctly, customer data provides tremendous business value across functions. Let’s look at some of the ways analyzing customer data and insights can directly drive business growth:
Analyzing granular insights into individual customer preferences, interests, and behaviors enables website personalization. Personalization uses customer data models to tailor messaging, offers, and experiences to demonstrated behaviors and preferences.
The implementation of analytical customer relationship management allows for leveraging advanced data analytics, enabling a more insightful understanding of customer behavior and preferences for informed decision-making and strategic planning. For example:
A unified customer database management helps determine the optimal target audiences and positioning for digital campaigns across channels. Marketers can segment customers based on attributes like demographics, interests, and past campaign interactions to allocate budgets accordingly.
Advanced customer analytics techniques help identify customers with the highest predictive churn risk based on behavioral indicators like decreased usage or negative sentiment.
Effective customer data management can uncover valuable insights into emerging market trends, customer preferences, and unmet needs. This information can be leveraged to identify new product or service offerings, enhance existing offerings, and ultimately drive revenue.
The customer data management process can directly inform revenue growth opportunities such as:
The above are just some examples. Ultimately, customer insights and data-based opportunities should drive all business decisions to maximize growth.
Customer data is a powerful asset that enables businesses to intimately understand their customers, provide personalized experiences, improve products and services, and optimize operations. However, collecting and managing customer data involves major privacy, security, consent, and transparency responsibilities.
Businesses can drive significant competitive advantage while avoiding data misuse by following best practices around customer data management, collection, storage, analysis, and application. The key is clearly defined purposes, rock-solid governance, and using analysis to inform business decisions and growth directly. With management and application, customer data becomes an invaluable long-term business asset.